HITCON CTF Quals 2015 CTFTIME Page. Most of the challenges were very tedious, and this is one of the challenges that we solved (Although we only managed to solve this after the CTF ended).
Simple
Points: 100
Category: Cryptography
Description Become admin!
http://52.69.244.164:51913
simple-01018f60e497b8180d6c92237e2b3a67.rb
md5: 4bd00c892d5e71f6d1d25d0bff2f49ec
Our solution
Given the source code of the website, we’re told to get admin. Looking at the source code provided, to be able to print the flag out, we have to get the conditon r[‘admin’] to be equal to true.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
#!/usr/bin/env ruby
require 'sinatra/base'
require 'sinatra/cookies'
require 'openssl'
require 'json'
KEY = IO.binread('super-secret-key')
FLAG = IO.read('/home/simple/flag').strip
class SimpleApp < Sinatra::Base
helpers Sinatra::Cookies
get '/' do
auth = cookies[:auth]
if auth
begin
auth = auth.b
c = OpenSSL::Cipher.new('AES-128-CFB')
c.decrypt
c.key = KEY
c.iv = auth[0...16]
json = c.update(auth[16..-1]) + c.final
r = JSON.parse(json)
if r['admin'] == true
"You're admin! The flag is #{FLAG}"
else
"Hi #{r['username']}, try to get admin?"
end
rescue StandardError
'Something wrong QQ'
end
else
<<-EOS
<html><body><form action='/' method='POST'>
<input type='text' name='username'/>
<input type='password' name='password'/>
<button type='submit'>register!</button>
</form></body></html>
EOS
end
end
post '/' do
username = params['username']
password = params['password']
if username && password
data = {
username: username,
password: password,
db: 'hitcon-ctf'
}
c = OpenSSL::Cipher.new('AES-128-CFB')
c.encrypt
c.key = KEY
iv = c.random_iv
json = JSON.dump(data)
enc = c.update(json) + c.final
cookies[:auth] = iv + enc
redirect to('/')
else
'Invalid input!'
end
end
end
It seems that the IV used as well as the encrypted json is kept in the client’s cookie, and that the same cookie is used to determine if you’re an admin. (This indicates that if we can spoof the encrypted json, we can become admin)


AES-128 in CFB mode has a block size of 16 bytes.
Simply put,
Ciphertext of block #1 = E(IV, key) ^ Plaintext
Therefore, with knowledge of plaintext and ciphertext, we are able to obtain E(IV, key) and to forge for the first block of cipher text.
With a username and password of b, the Plaintext of the first block will be
{"username":"b",
and we’ll use that knowledge to obtain our E(IV, key)
This is our exploit script that forges our first block to be:
{"admin": true }
and allows us to obtain our flag!
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
import requests
import urllib
def main():
original_cookie = "\xE9a\x89\xEC\xC7\x7C\xBC\x15\x92\xAD\xF8\x17\xF8\x40" \
"wV\xAB524\xF2\xF5UA\xE8\x1A\x29\xD4\xCB\xFA\xF6\xB3" \
"\x95h\x2B\x0D\xF4\xB9\xC8\xDB\xF8n\xB9o\xBES\x11d\xA3" \
"9\xA3c\x3Fi\xE7\xFA\x1C\xD0\xDBk\xDD\xD2_6\x06"
original_cookie = original_cookie.encode('hex')
iv = original_cookie[0:32]
first_16_byte_block = original_cookie[32:64]
print "IV: %s" % iv
print "First Block: %s" % first_16_byte_block
#Plain text of first 16 byte block.
plaintext ='{"username":"b",'
encrypted_iv = int(plaintext.encode('hex'),16) ^ int(first_16_byte_block,16)
encrypted_iv = hex(encrypted_iv)[2:-1]
print "Encrypted IV: %s" % encrypted_iv
#The text I want to forge in the first block.
forge_text = '{"admin": true }'
print 'Encrypting payload...'
payload = int(forge_text.encode('hex'),16) ^ int(encrypted_iv,16)
payload = hex(payload)[2:-1]
payload = iv + payload
print "PAYLOAD: %s" % payload
cookie = {"auth": payload.decode("hex")}
r = requests.get("http://52.69.244.164:51913/", cookies=cookie)
print "Flag: %s" % r.text
if __name__ == "__main__":
main()
Running the script gives us:
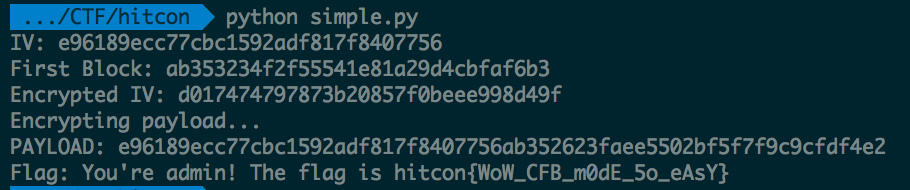
And we have our flag: hitcon{WoW_CFB_m0dE_5o_eAsY}
comments powered by Disqus